网络应用
主要功能
- MVC架构 (Model-View-Controller).
- 自动配置, 事先配置好的依赖包可以被注入到任何你指定的构造函数参数中或者结构体变量
- 依赖注入, 使用标签 `inject:“”` 或者构造函数来实现.
MVC架构介绍
Hiboot点MVC架构采用约定俗成的原则,尽量隐藏和业务无关的代码,开发者只需遵循少数几个简单的规则即可。
- 运行时动态配置及配置值注入
- 注册机制
- 依赖注入
在入门这个章节我们了解到了简单Hiboot网络应用,现在我们以hiboot-data gorm 示例代码为例,来详细讲解任何有效的基于Hiboot来编程。
MVC项目结构详解
下面是典型的hiboot MVC项目结构,接下来我们来对每个文件一一做详细说明。
.
├── config
│ ├── application-gorm.yml
│ ├── application-local.yml
│ ├── application.yml
│ ├── i18n
│ │ ├── en-US.ini
│ │ └── zh-CN.ini
│ ├── keygen.sh
│ └── ssl
│ ├── app.rsa
│ └── app.rsa.pub
├── main.go
├── main_test.go
├── controller
│ ├── user.go
│ └── user_test.go
├── entity
│ ├── user.go
│ └── user_test.go
└── service
├── user.go
└── user_test.goHiboot应用分两部分,外部配置及源代码。
外部配置
Hiboot要做可用于生产的应用框架,在设计之初就考虑到了需要适应不同的环境。在工作目录下的config文件夹包含了不同环境下的配置文件.
Hiboot允许将配置外部化,这样你就能够在不同的环境下使用相同的代码。
属性值可以通过`value:“”`标签直接注入到结构体中,
下面是具体的示例,假设你开发一个使用app.name属性的struct, 如下面例子:
type MyService struct {
AppName string `value:"${app.name}"`
}通用Application属性文件
Hiboot将从工作路径下的config文件夹中加载application.yml文件.
config/application.yml
application.yml定义应用项目、名称等基本信息
app:
project: examples
name: gorm-demo
profiles:
include:
- actuator
- locale
- logging
- gorm
logging:
level: infoapplication.yml字段说明
| 字段 | 描述 | 合法值 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| app.project | 项目名称 | 任意字符串 | examples |
| app.name | 应用名称 | 任意字符串 | gorm-demo |
| app.profiles.active | 当前环境配置 | local,dev,test,staging,prod | dev |
| profiles.include | starter的开关功能,⚠️ 如果没有包含进来,则该starter不会被初始化,相关依赖不能被注入 | starter包名 | actuator, locale, logging, gorm |
| logging.level | 定义日志级别 | debug,info,warn,error,fatal | info |
任何以某个字符名称为后缀的配置文件,有两种情况:
- 事先定义了相关环境变量,Hiboot会认为当前应用运行在不同的环境下,如
config/application-local.yml为本地开发环境,在本地电脑需要设置环境变量APP_PROFILES_ACTIVE为local - 引用了starter,可以将starter的属性值配置到
application.yml, 也可以将其配置到以starter包名为后缀的配置文件中,如本例的application-gorm.yml
config/application-local.yml
server:
port: 8081
logging:
level: debugapplication-local.yml 字段说明
| 字段 | 描述 | 合法值 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| server.port | 监听端口, 通常在本地开发应用时可能有多个应用同时运行,为例防止端口冲突,可以定义不同的端口 | 任意数字 | 8081 |
| logging.level | 定义日志级别 | debug,info,warn,error,fatal | info |
config/application-gorm.yml
gorm:
type: mysql
host: mysql-${app.profiles.active:dev}
port: 3306
database: ${app.name:test}
username: demo
password: fafUJCsVXf2Thj0d4n6UqNdX2PfI08fMyaNlrZhbJVVkghnZ+Zc/WCdITXflJpHZjYH5+LbLviy/6j9etPNwtdyAOXiqKI62itC6nDgp0Xlzu0qX8MwMIIAosUwaYpnflg23hRZnueKrq6SrEpkx4X+LWluDgHb2O5VfGGvHliE=
charset: utf8
parseTime: true
loc: Asia/Shanghai
config:
decrypt: trueapplication-gorm.yml字段说明
| 字段 | 描述 | 合法值 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| gorm.type | 数据库类型, 支持的有多种数据库 | mysql,postgres,sqlite3,mssql | mysql |
| gorm.host | 数据库地址,允许使用变量 mysql-${app.profiles.active} 如在本地开发环境,设置环境变量APP_PROFILES_ACTIVE 为 local,则实际值为mysql-local,添加一条DNS的A记录即可 |
任何合法DNS域名或IP地址(字符串类型) | mysql-${app.profiles.active} |
| gorm.port | 数据库端口 | 任何有效端口 | 3306 |
| gorm.database | 数据库名称 | 字符或变量 | ${app.name:test} |
| gorm.username | 数据库用户名 | 合法的数据库用户名 | dbuser |
| gorm.password | 数据库密码,如果gorm.config.decrypt为true,则为crypto加密过的数据库密码 | 字符串 | fafUJ … O5VfGGvHliE= |
| gorm.charset | 数据库字符集 | utf8,ascii | utf8 |
| gorm.parseTime | 是否解析时间 | true,false | true |
| gorm.loc | 本地时区 | 参考标准时区 | Asia/Shanghai |
| gorm.config.decrypt | 是否加密密码 | true,false | true |
main.go
和任何Go语言应用一样,Hiboot的程序入口为main包,包含两部分:引入用到的依赖包以及一个main函数。
为了解耦包与包之间的依赖关系,hiboot规定,依赖项采用注册,依赖注入的方式来解耦,故在main包里想要匿名引入MVC控制器
hidevops.io/hiboot-data/examples/gorm/controller, 如果使用到了其它第三方自动配置包(这里一般是指starter),而代码没有显式使用的,也要匿名引人,如:hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/starter/actuator,hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/starter/locale,hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/starter/loggingmain函数非常简单,只有一行代码
web.NewApplication().Run(),web包引自hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/app/webpackage main import ( _ "hidevops.io/hiboot-data/examples/gorm/controller" "hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/app/web" _ "hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/starter/actuator" _ "hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/starter/locale" _ "hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/starter/logging" ) func main() { web.NewApplication().Run() }
mian_test.go
main函数单元测试,TestRunMain第一行代码是 go main(), 我们起一个go routine来无阻塞的测试main函数,后面代码time.Sleep(200 * time.Millisecond)做个简单延时,可以用于main函数代码覆盖测试。
package main
import (
"testing"
"time"
)
func TestRunMain(t *testing.T) {
go main()
time.Sleep(200 * time.Millisecond)
}控制器 - controller/user.go
接下来我们来看看如何正确编写Hiboot的控制器,
控制器 userController 内嵌 at.RestController, 指明这是个RESTful控制器。
newUserController为userController的构造函数,实现依赖注入,在应用启动过程中, userService service.UserService 将被自动注入到 newUserController。
控制器是RESTful接口的入口,不同于其它Go语言网络应用框架,Hiboot控制器设计思路是尽可能的简单易用,省去路由配置代码,约定方法名即路由配置。如下userController的Post方法。
现针对各个方法作详细说明
| 方法 | 描述 | 合法值 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Get | GET请求 | Get或以大写开头的驼峰命名法则GetById | func (c *userController) GetById(id unit64) |
| Post | POST请求 | Post或以大写开头的驼峰命名法则PostUser | func (c *userController) Post(request *userRequest) |
| Put | PUT请求 | Put或以大写开头的驼峰命名法则PutUser | func (c *userController) Post(request *userRequest) |
| Delete | DELETE请求 | Delete或以大写开头的驼峰命名法则DeleteById | func (c *userController) DeleteById(id unit64) |
⚠️ 在函数 init() 必须注册 newUserController.
package controller
import (
"hidevops.io/hiboot-data/examples/gorm/entity"
"hidevops.io/hiboot-data/examples/gorm/service"
"hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/app"
"hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/app/web"
"hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/model"
"net/http"
)
// RestController
type userController struct {
at.RestController
userService service.UserService
}
func init() {
app.Register(newUserController)
}
// newUserController inject userService automatically
func newUserController(userService service.UserService) *userController {
return &userController{
userService: userService,
}
}
// Post POST /user
func (c *userController) Post(request *entity.User) (model.Response, error) {
err := c.userService.AddUser(request)
response := new(model.BaseResponse)
response.SetData(request)
return response, err
}
// GetById GET /id/{id}
func (c *userController) GetById(id uint64) (response model.Response, err error) {
user, err := c.userService.GetUser(id)
response = new(model.BaseResponse)
if err != nil {
response.SetCode(http.StatusNotFound)
} else {
response.SetData(user)
}
return
}
// GetById GET /id/{id}
func (c *userController) GetAll() (response model.Response, err error) {
users, err := c.userService.GetAll()
response = new(model.BaseResponse)
response.SetData(users)
return
}
// DeleteById DELETE /id/{id}
func (c *userController) DeleteById(id uint64) (response model.Response, err error) {
err = c.userService.DeleteUser(id)
response = new(model.BaseResponse)
return
}entity/user.go
这是业务逻辑模型。
package entity
type User struct {
Id uint64 `json:"id"`
Name string `json:"name"`
Username string `json:"username"`
Password string `json:"password"`
Email string `json:"email"`
Age uint `json:"age"`
Gender uint `json:"gender"`
}
func (u *User) TableName() string {
return "user"
}Model - service/user.go
service包实现业务逻辑。
我们定义了一个接口UserService,包含AddUser, GetUser, GetAll 和 DeleteUser方法。
userServiceImpl为接口UserService的具体实现。
通过引人hiboot-data/starter/gorm,即可自动注入 repository gorm.Repository到userServiceImpl
⚠️ 在函数 init() 必须注册 newUserService.
package service
import (
"errors"
"hidevops.io/hiboot-data/examples/gorm/entity"
"hidevops.io/hiboot-data/starter/gorm"
"hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/app"
"hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/utils/idgen"
)
type UserService interface {
AddUser(user *entity.User) (err error)
GetUser(id uint64) (user *entity.User, err error)
GetAll() (user *[]entity.User, err error)
DeleteUser(id uint64) (err error)
}
type userServiceImpl struct {
// add UserService, it means that the instance of UserServiceImpl can be found by UserService
UserService
repository gorm.Repository
}
func init() {
// register UserServiceImpl
app.Register(newUserService)
}
// will inject BoltRepository that configured in hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/starter/data/bolt
func newUserService(repository gorm.Repository) UserService {
repository.AutoMigrate(&entity.User{})
return &userServiceImpl{
repository: repository,
}
}
func (s *userServiceImpl) AddUser(user *entity.User) (err error) {
if user == nil {
return errors.New("user is not allowed nil")
}
if user.Id == 0 {
user.Id, _ = idgen.Next()
}
err = s.repository.Create(user).Error()
return
}
func (s *userServiceImpl) GetUser(id uint64) (user *entity.User, err error) {
user = &entity.User{}
err = s.repository.Where("id = ?", id).First(user).Error()
return
}
func (s *userServiceImpl) GetAll() (users *[]entity.User, err error) {
users = &[]entity.User{}
err = s.repository.Find(users).Error()
return
}
func (s *userServiceImpl) DeleteUser(id uint64) (err error) {
err = s.repository.Where("id = ?", id).Delete(entity.User{}).Error()
return
}运行网络应用程序
go run main.go输出结果如下:
______ ____________ _____
___ / / /__(_)__ /_______________ /_
__ /_/ /__ /__ __ \ __ \ __ \ __/
_ __ / _ / _ /_/ / /_/ / /_/ / /_ Hiboot Application Framework
/_/ /_/ /_/ /_.___/\____/\____/\__/ https://hidevops.io/hiboot
[INFO] 2018/10/23 23:37 Starting Hiboot web application gorm-demo on localhost with PID 28423
[INFO] 2018/10/23 23:37 Working directory: /Users/johnd/.gvm/pkgsets/go1.10/hidevops/src/hidevops.io/hiboot-data/examples/gorm
[INFO] 2018/10/23 23:37 The following profiles are active: local, [actuator locale logging gorm]
[INFO] 2018/10/23 23:37 Auto configure gorm starter
[INFO] 2018/10/23 23:37 Auto configure locale starter
[INFO] 2018/10/23 23:37 Auto configure logging starter
[INFO] 2018/10/23 23:37 The dependency graph resolved successfully
[INFO] 2018/10/23 23:37 connected to dataSource demo@mysql-local:3306/gorm_demo
[DBUG] 2018/10/23 23:36 GET: /health -> github.com/hidevops io/hiboot-data/vendor/hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/starter/actuator/controller/healthController.Get() and 2 more
[DBUG] 2018/10/23 23:36 DELETE: /user/id/{id} -> hidevops.io/hiboot-data/examples/gorm/controller/userController.DeleteById() and 2 more
[DBUG] 2018/10/23 23:36 GET: /user/id/{id} -> hidevops.io/hiboot-data/examples/gorm/controller/userController.GetById() and 2 more
[DBUG] 2018/10/23 23:36 GET: /user/all -> hidevops.io/hiboot-data/examples/gorm/controller/userController.GetAll() and 2 more
[DBUG] 2018/10/23 23:36 POST: /user -> hidevops.io/hiboot-data/examples/gorm/controller/userController.Post() and 2 more
Now listening on: http://localhost:8080
Application started. Press CMD+C to shut down.请求接口
让我们用httpie来请求接口
http GET localhost:8080/user/all?lang=zh-CN输出结果如下:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: 307
Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8
Date: Tue, 23 Oct 2018 15:38:41 GMT
Set-Cookie: app.language=zh-CN; Path=/; Expires=Tue, 23 Oct 2018 17:38:41 GMT; Max-Age=7200; HttpOnly
{
"code": 200,
"data": [
{
"age": 18,
"email": "john.doe@gmail.com",
"gender": 0,
"id": 209536579658580081,
"name": "John Doe",
"password": "poi321",
"username": "johnd"
},
{
"age": 25,
"email": "mike.phil@gmail.com",
"gender": 0,
"id": 209536656246571121,
"name": "Mike Phil",
"password": "iutg039",
"username": "mikep"
}
],
"message": "成功"
}单元测试
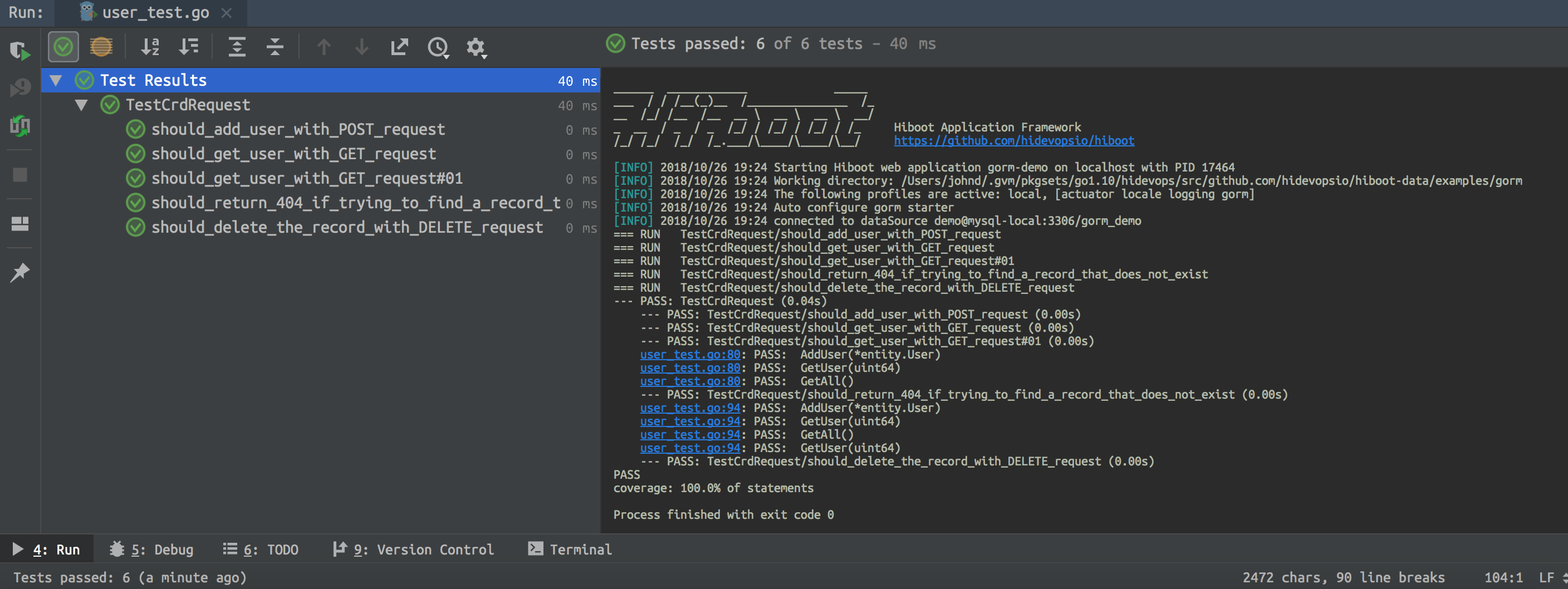
我说过,Hiboot从一开始就考虑到必须能用于生产环境,我们非常在意代码质量。你可以看我们集成了CI流程,代码必须通过严格的测试之后才会合并到主分支。这是Hiboot实时的代码测试覆盖率 . 那么,我们是怎样来做单元测试的呢?
首先,让我们来看main.go下面最简单的单元测试,
mian_test.go
为了简单起见, 我们用一个go routine 来跑main函数的测试 go main() 在这个单元测试用例 TestRunMain。当然这不是真正意义上的测试, 因为里面并没有assert语句,我们并不知道测试结果。
package main
import (
"testing"
"time"
)
func TestRunMain(t *testing.T) {
go main()
time.Sleep(200 * time.Millisecond)
}模拟测试 - controller/user_test.go
我们想测试 userController, 但是userController 依赖了 userSerivce,而userSerivce 又会连接真正的数据库,可是我们要做自动化测试,我们要做持续集成怎么办?当然我们可以使用模拟测试法。
我们使用模拟测试代码生成工具Mockery 来生成部分测试代码,以减轻我们写代码的负担。
首先,我们来安装Mockery
go get github.com/vektra/mockery/.../然后,为接口UserService生成模拟测试代码,当然你得到相应的文件夹下面去生成代码,你也可以指定文件夹,具体方法可以看Mockery的帮助文档(运行 mockery -h 查看)
# go to the directory where the UserService is.
cd $GOPATH/src/hidevops.io/hiboot-data/examples/gorm/service
# generate mocks for the interface UserService
mockery -name UserService接下来,你将会在项目下面($GOPATH/src/hidevops.io/hiboot-data/examples/gorm/service.)看到生成好的模拟测试代码。
// Code generated by mockery v1.0.0. DO NOT EDIT.
package mocks
import entity "hidevops.io/hiboot-data/examples/gorm/entity"
import mock "github.com/stretchr/testify/mock"
// UserService is an autogenerated mock type for the UserService type
type UserService struct {
mock.Mock
}
// AddUser provides a mock function with given fields: user
func (_m *UserService) AddUser(user *entity.User) error {
ret := _m.Called(user)
var r0 error
if rf, ok := ret.Get(0).(func(*entity.User) error); ok {
r0 = rf(user)
} else {
r0 = ret.Error(0)
}
return r0
}
// DeleteUser provides a mock function with given fields: id
func (_m *UserService) DeleteUser(id uint64) error {
ret := _m.Called(id)
var r0 error
if rf, ok := ret.Get(0).(func(uint64) error); ok {
r0 = rf(id)
} else {
r0 = ret.Error(0)
}
return r0
}
// GetAll provides a mock function with given fields:
func (_m *UserService) GetAll() (*[]entity.User, error) {
ret := _m.Called()
var r0 *[]entity.User
if rf, ok := ret.Get(0).(func() *[]entity.User); ok {
r0 = rf()
} else {
if ret.Get(0) != nil {
r0 = ret.Get(0).(*[]entity.User)
}
}
var r1 error
if rf, ok := ret.Get(1).(func() error); ok {
r1 = rf()
} else {
r1 = ret.Error(1)
}
return r0, r1
}
// GetUser provides a mock function with given fields: id
func (_m *UserService) GetUser(id uint64) (*entity.User, error) {
ret := _m.Called(id)
var r0 *entity.User
if rf, ok := ret.Get(0).(func(uint64) *entity.User); ok {
r0 = rf(id)
} else {
if ret.Get(0) != nil {
r0 = ret.Get(0).(*entity.User)
}
}
var r1 error
if rf, ok := ret.Get(1).(func(uint64) error); ok {
r1 = rf(id)
} else {
r1 = ret.Error(1)
}
return r0, r1
}Writing the unit test cases
接着我们就要来写相关的测试用例了,下面我们测试了POST, GET, DELETE几个方法,而其中并没有去连接数据库,但是能测试到userController的业务逻辑。
package controller
import (
"hidevops.io/hiboot-data/examples/gorm/entity"
"hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/app/web"
"hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/log"
"hidevops.io/hiboot/pkg/utils/idgen"
"github.com/stretchr/testify/assert"
"net/http"
"testing"
"hidevops.io/hiboot-data/examples/gorm/service/mocks"
"errors"
)
func init() {
log.SetLevel(log.DebugLevel)
}
func TestCrdRequest(t *testing.T) {
mockUserService := new(mocks.UserService)
userController := newUserController(mockUserService)
testApp := web.RunTestApplication(t, userController)
id, err := idgen.Next()
assert.Equal(t, nil, err)
testUser := &entity.User{
Id: id,
Name: "Bill Gates",
Username: "billg",
Password: "3948tdaD",
Email: "bill.gates@microsoft.com",
Age: 60,
Gender: 1,
}
// first, call mocks.UserService.AddUser
mockUserService.On("AddUser", testUser).Return(nil)
// then run the test that will call UserService.AddUser
t.Run("should add user with POST request", func(t *testing.T) {
// First, let's Post User
testApp.Post("/user").
WithJSON(testUser).
Expect().Status(http.StatusOK)
})
mockUserService.On("GetUser", id).Return(testUser, nil)
t.Run("should get user with GET request", func(t *testing.T) {
// Then Get User
// e.g. GET /user/id/123456
testApp.Get("/user/id/{id}").
WithPath("id", id).
Expect().Status(http.StatusOK)
})
mockUserService.On("GetAll").Return(&[]entity.User{*testUser}, nil)
t.Run("should get user with GET request", func(t *testing.T) {
// Then Get User
// e.g. GET /user/id/123456
testApp.Get("/user/all").
Expect().Status(http.StatusOK)
})
// assert that the expectations were met
mockUserService.AssertExpectations(t)
unknownId, err := idgen.Next()
assert.Equal(t, nil, err)
mockUserService.On("GetUser", unknownId).Return((*entity.User)(nil), errors.New("not found"))
t.Run("should return 404 if trying to find a record that does not exist", func(t *testing.T) {
// Then Get User
testApp.Get("/user/id/{id}").
WithPath("id", unknownId).
Expect().Status(http.StatusNotFound)
})
// assert that the expectations were met
mockUserService.AssertExpectations(t)
mockUserService.On("DeleteUser", id).Return(nil)
t.Run("should delete the record with DELETE request", func(t *testing.T) {
// Finally Delete User
testApp.Delete("/user/id/{id}").
WithPath("id", id).
Expect().Status(http.StatusOK)
})
}最后,我们来运行测试用例,